Tibial Tuberosity Fractures in Adolescents: Anatomo – Clinical Assessment and Treatment Results
Volume 10 | Issue 3 | September-December 2024 | Page: 12-18 | Ake YL, Ouattara SJJ, Bonny R, Kouassi-Dria AKS
DOI- https://doi.org/10.13107/ijpo.2024.v10.i03.202
Open Access License: CC BY-NC 4.0
Copyright Statement: Copyright © 2024; The Author(s).
Submitted: 28/10/2024; Reviewed: 10/11/2024; Accepted: 03/12/2024; Published: 10/12/2024
Authors: Ake YL [1], Ouattara SJJ [1], Bonny R [1], Kouassi-Dria AKS [1]
[1] Department of Paediatric Surgery, Cocody Teaching Hospital, Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Address of Correspondence
Dr. Ake Yapi Landry
Associate Lecturer, Department of Paediatric Surgery, Cocody Teaching Hospital, Abidjan, Ivory Coast
Email: akeyapilandry@yahoo.fr
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to describe the anatomo-clinical, therapeutic aspect of TT fractures and the results.
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted over a period of 5 years (01 January 2018 to 01 January 2023) in the Paediatric Surgery Department of the Teaching Hospital and at theInternational clinic. The epidemiological- clinical, anatomopathological, therapeutic, and the results variables of TT fractures were studied.
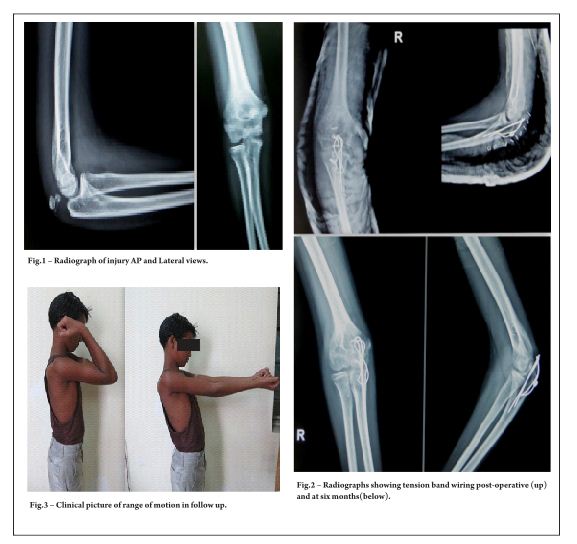
Results: Data from 10 cases were included in this study. All patients were male, and their mean age was 14.3 years [range: 11-15 years]. All fractures occurred during sports activities through indirect mechanisms. Fractures occurred on both the left and right sides of the knee. We have compiled fractures of type IB (2 cases), type IIB (03 cases), IIIA (01 case), type IIIB (03 cases), and type IV (01 case). All patients underwent open reduction and osteosynthesis. No complications occurred in any of the patients, and their long-term results were satisfactory.
Conclusion: TT fractures are uncommon in adolescents; however, they are common in sports that involve jumping. The indications for treatment are based on the modified Ogden classification. These fractures have a good prognosis, with full recovery of function and activity after consolidation.
Keywords: Fracture, Tibial tuberosity, Adolescence
References
1. Casas L, Romero I, Orivio G. Traitement de la fracture avulsion de la tubérosité tibiale antérieure chez les adolescents. Acta Ortop Mex2013;27: 160–69.
2. Behery OA, Feder OI, Beutel BG, et al. Combined Tibial Tubercle Fracture and Patellar Tendon Avulsion: Surgical Technique and Case Report. J Orthop Case Rep 2018; 8:18–22. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2250-0685.1090.
3. Wendell W, Symone M, Bryan V. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of Tibial Tubercle Avulsion Fractures in Adolescents. JBJS Rev 2020; 8: e0186. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.19.00186.
4. Aleilimar T, Leonardo J, Ulbiramar C. Anterior avulsion fracture of the tibial tuberosity in adolescents – Two case reports. Rev Bras Ortop 2016; 51:610–3. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2016.08.001.
5. Pranav C, Raja A, Sherlin L, et al. Imaging Review of Adolescent Tibial Tuberosity Fractures. Open J Med Imaging 2013; 3:90–6. doi:10.4236/ojmi.2013.33014.
6. Pretell-Mazzini J, Derek M, Jeffrey R. Outcomes and Complications of Tibial Tubercle Fractures in Pediatric Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Pediatr Orthop 2016; 36:440–6. doi:
10.1097/BPO.0000000000000488.
7. Watson-Jones R. Fractures and joint injuries. 5th ed. Baltimore, USA, Williams & Wilkins Company, 1979:1048–50.
8. Ogden JA, Tross RB, Murphy MJ. Fractures of the tibial tuberosity in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1980; 62:205–15.
9. Checa Betego N, Arvinius C, Cabadas G. Management of pediatric tibial tubercle fractures: is surgical treatment really necessary? J Orthop Surg Trauma 2019; 29:1073 9. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02390-x.
10. Reuter S, Mellerowicz H. Avulsionsverletzungen der proximalen Tibia. Der Orthopäde 2016; 45:226–32. doi:10.1007/s00132-016-3228-y.
11. Fnini S, Sirajhak M, Messoudi A. Fracture-avulsion négligée de la tubérosité tibiale antérieure. J Traumatol du Sport 2011; 28:257–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jts.2011.10.001.
12. Bombah FM, Nana T, Ekani BY, et al. Fracture-avulsion of tibial tubercle apophyseal in two Cameroonian adolescents. Trauma Case Rep 2021;35: 100525. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2021.100525.
13. Pace JL, McCulloch PC, Momoh EO, et al. Operatively TreatedType IV Tibial Tubercle Apophyseal Fractures. J Pediatr Orthop2013; 33:8–9. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3182968984.
14. Khoriati AA, Guo S, Thakrar R, et al. Bilateral atraumatic tibial tubercle avulsion fractures: case report and review of the literature. Injury 2015;46: 767–9. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2015.01.012.
15. Kunis GW, Berko JA, Shogan JC, et al. Tibial Tubercle Avulsion Fractures in Adolescents: A Narrative Review and Case Report. J Orthop & Orthopedic Surg. 2021; 2:12–8. doi: 10.29245/2767-5130/2021/3.1149.
16. Frey S, Hosalkar H, Cameron DB. Tibial tuberosity fractures in adolescents. J Child Orthop 2008; 2:469–74. doi: 10.1007/s11832-008-0131-z.
17. Brey JM, Conoley J, Canale ST, et al. Tibial Tuberosity Fractures in Adolescents: Is aPosterior Metaphyseal Fracture Component a Predictor of Complications? J Pediatr Orthop 2; 32:561–6. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e318263a370.
18. Franz P, Luderowski E, Tuca M. Tibial tubercle avulsion fractures in children. Curr Opin Pediatr 2020; 32:86–92. doi:10.1097/MOP.0000000000000870.
19. Bauer T, Milet A, Odent T. Fracture-avulsion de la tubérosité tibiale antérieure chez l’adolescent À propos de 22 cas et revue de la littérature. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 2005; 91:758–67
20. Hannouche D, Duparc F, Beaufils P. The arterial vascularization of the lateral tibial condyle: anatomy and surgical applications. Surg Radiol Anat 2006; 28:38–45. doi: 10.1007/s00276-005-0044-1.
21. Driss Jeddi, El Maqrout A, Kharmaz M. Avulsion fracture of anterior tibial tuberosity in a sporty adolescent. Sch J App Med Sci2019; 7(2):728–9. doi: 10.21276/sjams.2019.7.2.61.
22. Checa Betegón P, Arvinius C, Cabadas González M, et al.Management of pediatric tibial tubercle fractures: Is surgicaltreatment really necessary? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol2019; 29:1073–9. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02390-x.
23. Jakoi A, Freidl M, Old A, et al. Tibial Tubercle AvulsionFractures in Adolescent Basketball Players. Orthopedics2012; 35:692–6. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20120725-07.
24. Rodriguez I, Sepúlveda M, Birrer E, et al. Fracture of the anterior tibial tuberosity in children. EFORT Open Rev 2020; 5:260–7. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190026.
25. Mubarak SJ, Kim JR, Edmonds EW, et al. Classification of proximal tibial fractures in children. J Child Orthop 2009; 3:191–7. doi: 10.1007/s11832-009-0167-8.
26. Pandya NK, Edmonds EW, Roocroft JH, et al. Tibial tubercle fractures: complications, classification, and the need for intra- articular assessment. J Pediatr Orthop 2012; 32:749–59. doi:10.1097/BPO.0b013e318271bb05.
27. Clarke DO, Franklin SA, Wright DE. Avulsion fracture of the tibial tubercle associated with patellar tendon avulsion. Orthopedics2016;39: e561–4. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20160414-02.
28. Goh TC, Abdul Halim AR. Avulsion Fractures of the Bilateral Tibial Tuberosity in an Adolescent: A Case Report and Literatures Review. European Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Sciences2018; 4:73–5. doi: 10.11648/j.ejcbs.20180406.12.
29. Pesl T, Havranek P. Acute tibial tubercle avulsion fractures in children: selective use of the closed reduction and internal fixation method. J Child Orthop. 2008; 2:353–6. doi: 10.1007/s11832-008-0126-9.
30. Nicolini AP, Carvalho RT, Ferretti M, et al. Simultaneous bilateral tibial tubercle avulsion fracture in a male teenager: case report and literature review. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2018; 27:40–6. doi:10.1097/BPB.0000000000000313.
31. Zaizi A, El Yaacoubi T, Chafry B, et al. Tibial tubercle avulsion fractures in school sports injury: A case report. Int J Surg Case Rep2019; 58:30–2. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.03.017.
32. Ares O, Seijas R, Cugat R. Treatment of fractures of the tibial tuberosity in adolescent soccer players. Acta Orthop Belg 2011; 77:78–82.
33. Arkader A, Schur M, Refakis C, et al. Unicortical Fixation is Sufficient for Surgical Treatment of Tibial Tubercle Avulsion Fractures in Children. J Pediatr Orthop 2019;39: e18–e22. doi:10.1097/BPO.0000000000001269.
34. Behery OA, Feder OI, Beutel BG, et al. Combined tibial tubercle fracture and patellar tendon avulsion: Surgical technique and case report. J Orthop Case Rep. 2018; 8:18–22. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2250- 0685.1090.
35. Fernández EV, de la Mora García AS. Avulsion fracture of the anterior tuberosity of the tibia in adolescents. Cuban Journal of Orthopedics and Traumatology 2017; 30:1–2.
36. Buckinx F, Bornheim S, Remy G, et al. French translation and validation of the “Anterior Knee Pain Scale” (AKPS) Disabil Rehabi2019;41:1089–94. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2017.1419288.
| How to Cite this Article: Ake YL, Ouattara SJJ, Bonny R, Kouassi-Dria AKS | Tibial Tuberosity Fractures in Adolescents: Anatomo – Clinical Assessment and Treatment Results | International Journal of Paediatric Orthopaedics | September-December 2024; 10(3): 12-18. |